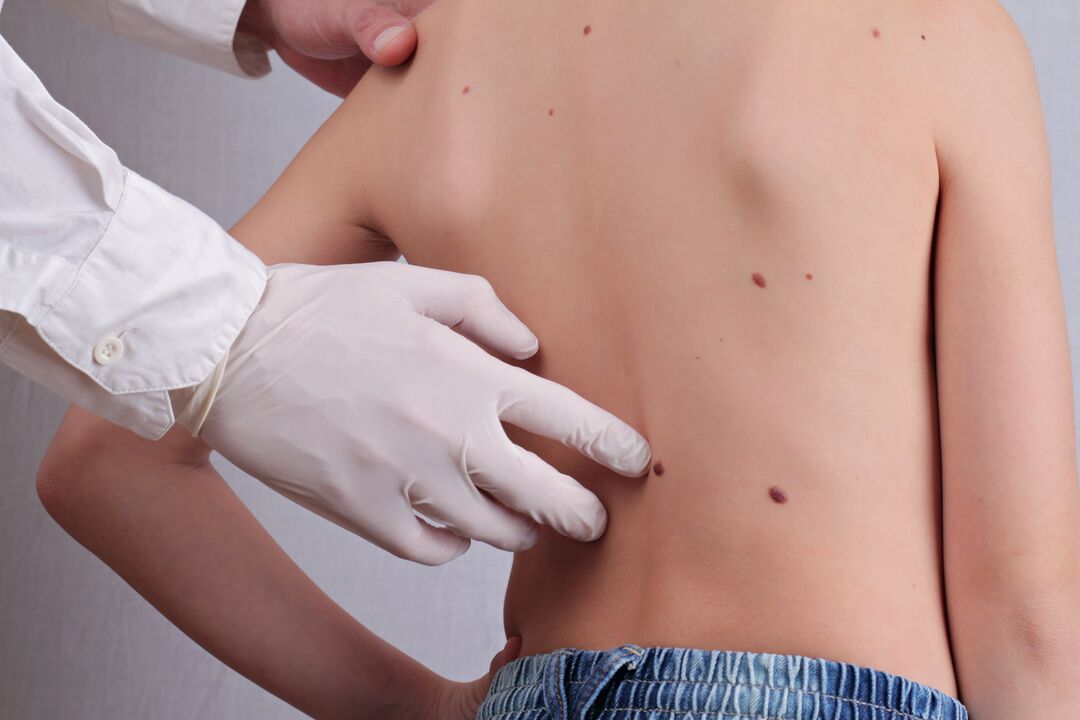
What happened
type
simple (vulgar)
Common warts are most common on the upper limbs, especially the hands. However, the growth can cover the body, palms of hands, toes, and other surfaces.
filamentous
After the age of 45 in this breed, papillomas will appear in areas where the skin is thin. In particular, they form in the armpits, sternum in women and men, and in the neck area.
flat
tip
soles of feet
juvenile
localization
Generally speaking, papillomatosis is a systemic disease in which papillomas appear throughout the body.
reason
- unprotectedsexualcommunication;
- Frequent gender changepartner;
- weakenimmunity;
- disobey rulessanitaryRegulation of oral and intimate areas;
- Organ diseasesgastrointestinal tract- Intestine;
- violationexchangeprocess;
- IncorrectNutrition;
- receptioncytostaticor hormonal drugs.
route of infection
sex
domestic
touch
from mother to fetus
diagnosis
clinical examination
colposcopy
PCR analysis
Cytological examination
Histology
screening test
treat
drug
- vitamin and mineral complex;
- Immunostimulants.
surgical
freeze damage
electrocoagulation
Experts first use rings to remove the stem of the structure, and then cauterize the element itself. During the working process, the capillaries coagulate simultaneously, thus preventing bleeding.
radiosurgery
laser
The papilloma is burned by exposing it to a laser beam, causing the cells to vaporize layer by layer and completely removing the element.
diet
When to delete
- positivehighWarts, which may indicate a more serious medical condition in the body;
- planningPregnant, because against the background of hormonal changes, the risk of developing benign and malignant tumors increases.
Why are they dangerous?
Prognosis after resection
prevention
- Only process protectedgender;
- Use your own items exclusivelyhealth;
- regular reinforcementimmunity;
- Eat quality, healthy foodproduct;
- receive medical treatmenttake an examFor preventive purposes, at least once a year.















